1/8ページ
ダウンロード(1.2Mb)
このカタログについて
| ドキュメント名 | Viscosity Measurement Series |
|---|---|
| ドキュメント種別 | 製品カタログ |
| ファイルサイズ | 1.2Mb |
| 取り扱い企業 | 柴田科学株式会社 (この企業の取り扱いカタログ一覧) |
この企業の関連カタログ

このカタログの内容
Page1
Viscosity Measurement Series
Constant-Temperature Baths for Viscometers
Glass Viscometers ((Ass per JJIIS K 2283 3000))
Made in Japan
Along with the growth of the petrochemistry, polymer
chemistry, and other industries involving viscous
materials, viscosity measurements are increasingly
being performed for a variety of fluids.
The advanced glass manufacturing technology of
SIBATA SCIENTIFIC TECHNOLOGY, Ltd.
allows us to provide support for highly precise viscosity
measurements.
Page2
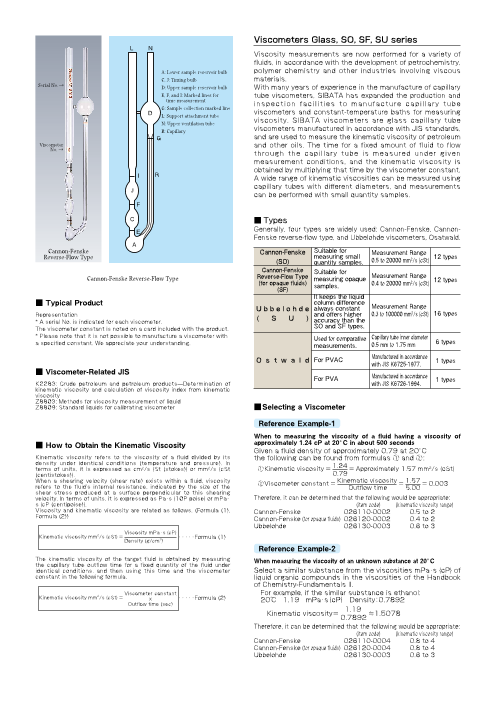
Viscometers Glass, SO, SF, SU series
L N
Viscosity measurements are now performed for a variety of
fluids, in accordance with the development of petrochemistry,
A: Lower sample reservoir bulb polymer chemistry and other industries involving viscous
C, J: Timing bulb materials.
Serial No. → D: Upper sample reservoir bulb With many years of experience in the manufacture of capillary
E, F, and I: Marked lines for tube viscometers, SIBATA has expanded the production and
time measurement inspection faci l i t ies to manufacture capi l lary tube
G: Sample collection marked line
D L: Support attachment tube viscometers and constant-temperature baths for measuring
N: Upper ventilation tube viscosity. SIBATA viscometers are glass capillary tube
R: Capillary viscometers manufactured in accordance with JIS standards,
G and are used to measure the kinematic viscosity of petroleum
Viscometer and other oils. The time for a fixed amount of fluid to flow
No. →
through the capil lary tube is measured under given
measurement conditions, and the kinematic viscosity is
obtained by multiplying that time by the viscometer constant.
I R A wide range of kinematic viscosities can be measured using
J capillary tubes with different diameters, and measurements can be performed with small quantity samples.
F
C ■Types
E Generally, four types are widely used: Cannon-Fenske, Cannon-
Fenske reverse-flow type, and Ubbelohde viscometers, Osatwald.
A
Cannon-Fenske Cannon-Fenske Suitable for measuring small Measurement Range Reverse-Flow Type
(SO) quantity samples. 0.5 to 20000 mm2/s {cSt}
12 types
Cannon-Fenske Suitable for
Cannon-Fenske Reverse-Flow Type Reverse-Flow Type measuring opaque Measurement Range (for opaque fluids) samples. 0.4 to 20000 mm
2/s {cSt} 12 types
2612-Z3 (SF) It keeps the liquid
■ Typical Product column difference
U b b e l o h d e always constant Measurement Range
Representation and offers higher 0.3 to 100000 mm2/s {cSt} 16 types
* A serial No. is indicated for each viscometer. ( S U ) accuracy than the
The viscometer constant is noted on a card included with the product. SO and SF types.
* Please note that it is not possible to manufacture a viscometer with Used for comparative Capillary tube inner diameter
a specified constant. We appreciate your understanding. measurements. 0.5 mm to 1.75 mm 6 types
O s t w a l d For PVAC Manufactured in accordance with JIS K6725-1977. 1 types
■ Viscometer-Related JIS
For PVA Manufactured in accordance 1 types
K2283: Crude petroleum and petroleum products—Determination of with JIS K6726-1994.
kinematic viscosity and calculation of viscosity index from kinematic
viscosity
Z8803: Methods for viscosity measurement of liquid
Z8809: Standard liquids for calibrating viscometer ■Selecting a Viscometer
Reference Example-1
When to measuring the viscosity of a fluid having a viscosity of
■ How to Obtain the Kinematic Viscosity approximately 1.24 cP at 20°C in about 500 seconds
Given a fluid density of approximately 0.79 at 20°C
Kinematic viscosity refers to the viscosity of a fluid divided by its the following can be found from formulas ① and ②:
density under identical conditions (temperature and pressure). In
terms of units, it is expressed as cm2/s {St (stokes)} or mm2/s {cSt ①Kinematic viscosity = 1.24 = Approximately 1.57 mm2/s {cSt}
(centistokes)}. 0.79
When a shearing velocity (shear rate) exists within a fluid, viscosity Kinematic viscosity 1.57
refers to the fluid's internal resistance, indicated by the size of the ②Viscometer constant = = = 0.003
shear stress produced at a surface perpendicular to this shearing
Outflow time 5.00
velocity. In terms of units, it is expressed as Pa・s {10P poise} or mPa・ Therefore, it can be determined that the following would be appropriate:
s {cP (centipoise)}. (item code) (kinematic viscosity range)
Viscosity and kinematic viscosity are related as follows. (Formula (1), Cannon-Fenske 026110-0002 0.5 to 2
Formula (2)) Cannon-Fenske (for opaque fluids) 026120-0002 0.4 to 2
Ubbelohde 026130-0003 0.6 to 3
Viscosity mPa・s {cP}
Kinematic viscosity mm2/s {cSt} = 3 ・・・・・Formula (1)Density (g/cm )
Reference Example-2
The kinematic viscosity of the target fluid is obtained by measuring
the capillary tube outflow time for a fixed quantity of the fluid under When measuring the viscosity of an unknown substance at 20°C
identical conditions, and then using this time and the viscometer Select a similar substance from the viscosities mPa・s {cP} of
constant in the following formula. liquid organic compounds in the viscosities of the Handbook
of Chemistry-Fundamentals II.
2 Viscometer constant For example, if the similar substance is ethanol:Kinematic viscosity mm /s {cSt} = x ・・・・・Formula (2) 20℃ 1.19 mPa・s{cP} Density:0.7892
Outflow time (sec)
K i ne m at i c v i s c o s i t y 1.19 = 0 . 78 9 2 ≒1.5078
Therefore, it can be determined that the following would be appropriate:
(item code) (kinematic viscosity range)
Cannon-Fenske 026110-0004 0.8 to 4
Cannon-Fenske (for opaque fluids) 026120-0004 0.8 to 4
Ubbelohde 026130-0003 0.6 to 3
Page3
■Viscosity and Kinematic Viscosity of Distilled Water ■Standard Fluids Used for Viscosity Measurement
(excerpt from JIS Z8803: 2011) (excerpt from JIS Z8803: 2011)
Temperature °C Viscosity mPa・s Kinematic Viscosity ㎜2/s
(1) If the viscosity is to be measured using the comparative
0 1.7906 1.7909 measurement method, the viscometer must be calibrated using
5 1.5185 1.5186 a standard fluid with a known viscosity or kinematic viscosity.
10 1.3064 1.3068 (2) As standard fluids for viscosity, use the standard fluids for viscometer calibration specified in JIS Z8809, and distilled
15 1.1378 1.1388 water at the temperatures shown in the table at left.
20 1.0016 1.0034 The table at left shows the viscosity and kinematic viscosity of
distilled water at various temperatures.
25 0.8899 0.8925
(3) For other standard fluids for viscosity, you can use fluids of
30 0.7970 0.8005 which the viscosity or kinematic viscosity value is obtained by
35 0.7189 0.7232 the absolute measurement method, or fluids of which the
40 0.6524 0.6576 viscosity value is obtained by the comparative measurement method using distilled water.
45 0.5960 0.6019
50 0.5469 0.5535 ■Standard Fluids for Viscometer Calibration
55 0.5043 0.5116 (excerpt from JIS Z8809: 2011)
60 0.4668 0.4748 Standard fluids for viscometer calibration are stipulated in JIS Z
8809. Their types and approximate values for kinematic
65 0.4338 0.4424 viscosity are shown in the table. Note that the determined value
70 0.4045 0.4137 for kinematic viscosity for each standard fluid is listed in the
75 0.3784 0.3882 performance guarantee that is provided with the standard fluid.
80 0.3550 0.3653 Kinematic Viscosity Approximate Value mm2/s {cSt}
Types
85 0.3340 0.3448 20℃ 25℃ 30℃ 40℃
90 0.3150 0.3263 JS 2.5 2.5 2.1 1.8
95 0.2977 0.3095 JS 5 5.0 3.9 3.2
100 0.2821 0.2943 JS 10 10 7.4 5.7
※ The values in this table are established with a viscosity of JS 20 20 14 10
1.0016 mPa・s at 20.00 °C as the standard. JS 50 50 32 21
JS 100 100 59 38
JS 200 200 110 66
JS 500 500 260 150
JS 1000 1000 500 270
JS 2000 2000 940 480
JS 14000 14000 5500 2400
JS 52000 52000 20000 8500
JS160000 160000 100000
※1㎝2/{s St}=100㎜2/{s cSt}
■Document
TEST CERTIFICATE
CERTIFICATE OF TARCEABILITY
TARCEABILITY CHART
Page4
Viscometer Cannon-Fenske (SO)
Manufactured in accordance with JIS K2283-2000.
With these viscometers, the viscosity is obtained by
measuring the time for a fixed quantity sample (the volume
between marked lines E and F) to flow out a capillary tube.
They are suitable for measuring the kinematic viscosity of
particularly small quantity samples. The 12 types shown in
the table below enable the measurement of kinematic
viscosities ranging from 0.5 mm2/s {cSt (centistokes)} to
20000 mm2/s {cSt (centistokes)}. (Constant table provided)
With these viscometers, the center of the timing bulb and
the sample reservoir bulb are positioned on the same central
axis in order to minimize measurement errors from tilt.
These viscometers are generally widely used.
Item Code Viscometer
Viscometer Constant Kinematic viscosity
No. (approximate value) measurement range㎜2/s2{cSt/s} ㎜2/s{cSt}
026110-0002 25 0.002 0.5 to 2
-0004 50 0.004 0.8 to 4
-0008 75 0.008 1.6 to 8
-0015 100 0.015 3 to 15
-0035 150 0.035 7 to 35
-01 200 0.1 20 to 100
-025 300 0.25 50 to 250
-05 350 0.5 100 to 500
-12 400 1.2 240 to 1200
-25 450 2.5 500 to 2500
-8 500 8 1600 to 8000
Viscometer Cannon-Fenske (SO) -20 600 20 4000 to 20000
■ Selection Procedure
(1) From the table, select a viscometer that has an outflow time between
200 seconds (250 seconds for Cannon-Fenske viscometer No. 25) and
1,000 seconds.
(2) See Reference Example-1 and Reference Example-2 on page 2.
L N
■Selecting a Viscometer
[Method of Measurement] (As per JIS K2283: 2000)
D F (1) As shown in Fig. 2, insert tube N into the sample with the
viscometer upside down. Apply suction through tube L so
E that the sample is drawn up to marked line F.
(2) Quickly restore the viscometer to the orientation in Fig. 1.
C E Wipe the sample off the outside of tube N. The sample will
flow out and collect in sample reservoir bulb A.
F (3) Place the viscometer in the constant-temperature bath.
At this point, position the viscometer so that the centers of
sample reservoir bulb A, timing bulb C, and upper sample bulb
D are aligned on the same straight line, and leave it to settle
until the sample reaches the prescribed temperature.
(4) Apply pressure through tube L or apply suction through
A tube N unti l the upper level of the f luid sample is
N approximately 5 mm above E.
L (5) Allow the sample to flow down naturally. Read out the
outflow time from E to F in increments of 0.1 seconds. If the
Sample outflow time is less than 200 seconds (less than 250
seconds for viscometer No. 25) or more than 1000 seconds,
choose another viscometer and repeat the procedure from
第1図 第2図 step (1).
Fig. 1 Fig. 2 For the calculation procedure, refer to JIS K2283:2000.
2611-Z1 2611-Z2
Page5
Viscometer Cannon-Fenske (for opaque fluids)
Reverse-Flow Type (SF)
These viscometers are generally used for kinematic viscosity
measurements of opaque samples.
The 12 types shown in the table below enable the
measurement of kinematic viscosities ranging from 0.4 mm2/
s {cSt (centistokes)} to 20000mm2/s {cSt (centistokes)}.
(Constant table provided)
With reverse-flow viscometers, the viscosity is obtained by
measuring the time for the sample to flow into a timing bulb,
which is provided at the lower section of the viscometer.
These viscometers are particularly suited to measurements
of opaque fluids since the sample flows into a dried timing
bulb. Moreover, there is no effect produced by the sample
remaining on the walls inside the timing bulb, so they are also
suited to viscosity measurements of high viscosity fluids.
Note that the time measurement can be made twice.
Viscometer Viscometer Constant Kinematic viscosity Item Code No. (approximate value) measurement range㎜2/s2{cSt/s} ㎜2/s{cSt}
026120-0002 25 0.002 0.4 to 2
-0004 50 0.004 0.8 to 4
-0008 75 0.008 1.6 to 8
-0015 100 0.015 3 to 15
-0035 150 0.035 7 to 35
-01 200 0.1 20 to 100
-025 300 0.25 50 to 250
-05 350 0.5 100 to 500
-12 400 1.2 240 to 1200
-25 450 2.5 500 to 2500
-8 500 8 1600 to 8000
-20 600 20 4000 to 20000 Viscometer Cannon-Fenske Reverse-Flow Type (SF)
■ Selection Procedure
(1) From the 12 types spanning a kinematic viscosity measurement range
of 0.4 mm2/s {cSt} to 20000 mm2/s {cSt}, select an appropriate viscometer.
At the same time, select a viscometer that has an outflow time between L N
200 seconds and 1,000 seconds. E
(2) See Reference Example-1 and Reference Example-2 on page 2.
F
■Selecting a Viscometer D
[Method of Measurement] (As per JIS K2283: 2000) I
(1) As shown in Fig. 2, insert tube N into the sample with the
viscometer upside down. Apply suction through tube L so G
that the sample is drawn up to marked line G.
(2) Return the viscometer to the orientation shown in Fig. 1. G
Wipe the sample off the outside of tube N, and insert the
rubber tube (about 50 mm in length).
The sample flows out of the capillary tube. When the content I
in sample reservoir bulb A reaches about 1/2, use a
pinchcock to seal the rubber tube to prevent any further D
sample outflow.
(3) Position the viscometer vertically in the constant- F
temperature bath, so it reaches the prescribed temperature.
(4) When the settling time has elapsed, open sealed tube N.
Measure the time for the sample to flow from E to F. Then
read out the outflow time from F to I in increments of 0.1 E N
seconds. L
If the outflow time is less than 200 seconds or more than A
1000 seconds, choose another viscometer and repeat the Sample
procedure from step (1).
For the calculation procedure, refer to JIS K2283:2000. 第2図第1図
Fig. 1 Fig. 2
2612-Z1 2612-Z2
Page6
Viscometer Ubbelohde (SU)
With Ubbelohde viscometers, the viscosity is obtained by
placing an appropriate quantity of the sample in the
viscometer, and then measuring the time required for the
sample in timing bulb C (the quantity between marked lines
m1 and m2) to flow through the capillary tube. These are
standard kinematic viscometers that do not require
correction for differences in surface tension.
The 16 types shown in the table below enable the
measurement of kinematic viscosities ranging from 0.3
mm2/s {cSt (centistokes)} to 100000 mm2/s {cSt
(centistokes)}. (Constant table provided)
They keep the liquid column difference always constant and
offer higher accuracy than the SO and SF types.
Viscometer Constant Kinematic viscosity
Item Code ViscometerNo. (approximate value) measurement range㎜2/s2{cSt/s} ㎜2/s{cSt}
026130-0001 0 0.001 0.3 to 1
-0003 0C 0.003 0.6 to 3
-0005 0B 0.005 1 to 5
-001 1 0.01 2 to 10
-003 1C 0.03 6 to 30
-005 1B 0.05 10 to 50
-01 2 0.1 20 to 100
-03 2C 0.3 60 to 300
-05 2B 0.5 100 to 500
-1 3 1 200 to 1000
-3 3C 3 600 to 3000
-5 3B 5 1000 to 5000
-10 4 10 2000 to 10000
-30 4C 30 6000 to 30000
-50 4B 50 10000 to 50000
Viscometer Ubbelohde (SU) -100 5 100 20000 to 100000
■Selecting a Viscometer
[Method of Measurement] (As per JIS K2283: 2000)
L N (1) From the 16 types spanning a kinematic viscosity
M measurement range of 0.3 mm2/s {cSt} to 100000 mm2/s
{cSt}, select a viscometer indicating an outflow time between
200 seconds (300 seconds for Ubbelohde viscometer No. 0)
LM N and 1000 seconds.
(2) Tilt the viscometer slightly, allowing the sample to flow in
through tube L until the fluid level of the sample is between
D marked lines m3 and m4 in sample reservoir bulb A. When
the viscometer is positioned vertically, the fluid level must
m not exceed marked line m3 due to the outflow of sample 1
adhering to tube L. Ensure that no bubbles enter the tube
C connecting A and B.
m2 (3) Position the viscometer in the constant-temperature
bath, and allow it to reach the prescribed temperature.
(4) When the settling time has elapsed, close tube M with
your fingers. Apply suction through tube N (or apply pressure
through tube L for volatile samples), raising the sample until
the upper fluid level exceeds m1 (approximately 8 mm).
(5) Stop applying suction or pressure. Open tube M and then
immediately seal tube N with your fingers. When the sample
flows out of the bottom end of the capillary tube, release
m3 B your fingers, and allow the sample to flow out naturally.
m4 (6) Read out the sample outflow time from m1 to m2 in
increments of 0.1 seconds. If the outflow time is less than
200 seconds (less than 300 seconds for viscometer No. 0)
A or more than 1000 seconds, choose another viscometer and
repeat the procedure from step (1).
For the calculation procedure, refer to JIS K2283:2000.
2613-Z1
Page7
Viscometer Ostwald (Relative Viscometer)
Ostwa l d v i scomete rs a r e used f o r compa ra t i v e
measurements.
Use a pipette to place 5 mL to 8 mL (always a fixed volume)
of the fluid sample in the lower bulb shown in the figure at
right.
Immerse the viscometer in the viscometer temperature- A
constant bath so that the liquid level of the bath reaches
above the marked line A. Apply suction until the fluid sample
is above marked line A. Then allow it to flow down naturally.
Measure the time taken by the fluid sample to flow down from
marked line A to B through the capillary tube. Using the same B
procedure, measure a standard fluid of known viscosity, being
careful that the volume of fluid placed in the lower bulb is
identical.
●Types no. 1 to 6 are available with different capillary tube diameters.
●These are relative viscometers for comparative measurements.
The bulb capacity is approximately 3mL.
Item Code Viscometer Capillary Tube Inner Diameter No. (approximate) mm
026300-1 1 0.5
-2 2 0.75
-3 3 1
-4 4 1.25
-5 5 1.5
-6 6 1.75
Note: No measured viscometer constant is provided, so kinematic
viscosity measurements are impossible with these viscometers.
026300- Viscometer Ostwald
2630-Z1
Viscometer Ostwald for Polyvinyl Acetate(PVAC)
10 mL of the sample is placed in the Ostwald viscometer.
The viscometer is then immersed in a constant-temperature
bath at 30 ±0.1 C and is used to measure the relative
viscosity with respect to benzene at the same temperature.
The outflow time for water at 30 °C is 120 ±20 seconds. A
●Capillary tube inner diameter: 0.48 to 0.52 mm
Manufactured in accordance with JIS K6725-1977. B
Item Code Product Name Applications
026330-1 Viscometer Ostwald For PVAC
Viscometer Ostwald for Polyvinyl Alcohl(PVA)
10 mL of the sample is placed in the Ostwald viscometer.
The viscometer is then immersed in a constant-temperature
bath at 30 ±0.1 °C and is used to measure the relative
viscosity with respect to water at the same temperature.
The outflow time for water at 30 °C is 100 ±20 seconds.
●Capillary tube inner diameter: 0.57 to 0.60 mm
Manufactured in accordance with JIS K6726-1994.
Item Code Product Name Applications
026340-1 Viscometer Ostwald For PVA
026330-1
026340-1 Viscometer Ostwald
2633-Z1
Page8
VB-3T Water Bath for Viscometers with 6
Suspension Clamps (With Timer)
This water bath can be used for measuring kinematic viscosity
using Cannon-Fenske, Cannon-Fenske reverse-flow type,
Ubbelohde, and Ostwald viscometers.
F e a t u r e s
● This constant-temperature bath provides highly accurate
temperature control, thanks to a high resolution digital
temperature controller and propeller pump.
●Three stopwatches are built in.
● A total of six viscometers, four Cannon-Fenske and two
Ubbelohde, can be suspended inside.
●It can offer stable temperature control even at close to room
temperature, with the cooling pipe provided inside the bath.
(A separate cool water circulator is required.)
●For information on glass viscometers, see page 2-7.
■Spare Parts
Item Code Product Name Applications
051260-0301 Viscometer mounting bracket (3 holes) For Ubbelohde
-0302 Viscometer mounting For Cannon-Fenske, S p e c i f i c a t i o n s bracket (2 holes) Ostwald
Item code 051260-031
Model VB-3T
Number of viscometers suspendable 6
Temperature settings range From room temperature to 85 °C※1
Operating ambient temperature +5℃ to +35℃
Accuracy of temperature control ±0.1℃(when used in constant temperature room)
Accuracy of temperature distribution ±0.1℃(when used in constant temperature room)
Temperature Main heater Digital temperature indicating controller (PID control method)adjustment Display resolution: 0.01℃
method Sub-heater Liquid expansion type temperature controller (ON/OFF)
Heater Main heater 300 W × 2, SUS316LSub-heater 300 W × 2, SUS316L
Agitation motor Induction motor, 4-pole, 15W
Temperature sensor Pt100Ω
Thermometer 100℃ in 1/10℃ graduations※2
Number of measured CH 3 channels (2-mode type)
Stopwatches Display method LED, 5 digits
Measurement range 0~9999.9 sec
Drain bulb Nozzle outer diameter, 10.5 mm
Cold water supply port Nozzle outer diameter, 10.5 mm
Unit protection functions Earth leakage breaker, overheat protection
1 glass rod thermometer※2、
Accessories 1 thermometer holder,
Viscometer mounting brackets (3 holes × 2, 2 holes × 4)
Dimensions Bath 335 (W) × 180 (D) × 315 (H) mm, Approx. 19 LMain Unit 530 (W) × 225 (D) × 420 (H) mm (excluding protrusions and motor)
Weight Approx. 23 kg
Power Supply 100 V AC 50/60 Hz, 14 A
*1: If the temperature to which to adjust is near room temperature, a separate cool water circulator needs to be connected.
*2: The purpose of this thermometer is for checking the temperature of the water bath for viscometers alone. If necessary, a separate JIS standard thermometer should be acquired.
Note 1: This product is not explosion-proof.
Note 2: The specifications and external appearance of this product are subject to change without notice in the interest of product improvement.
Viscometer Storage Case
This wooden storage case is designed to organize and store
Cannon-Fenske, Cannon-Fenske reverse-flow type, and
Ubbelohde viscometers. Four viscometers can be packed into
a single case.
Item Code Number Storable Specifications
026880-01 4 One level, with cover
Specifications, and appearance described in this document are based on information as of January 18, 2017. They are subject to change without notice for improvement of the product.
1-1-62, Nakane Soka-City, Saitama, Japan
TEL:+81-48-933-1582 FAX:+81-48-933-1591
E-mail:overseas@sibata.co.jp
http://www.sibata.co.jp/english/
201701K