1/45ページ
ダウンロード(2.9Mb)
切削工具2023~2024カタログのご案内です。
掲載内容
・エンドミル各部の名称とエンド外径について
・エンドミルの刃形と切削性
・エンドミルの切削条件の求め方
・エンドミル使用上のご注意
・エンドミル加工のトラブルと原因対策
・フライス工具の各部の名称と刃先角度の役割
・フライス用インサート各部の名称と役割
・フライス加工切削条件の選び方
・フライス加工におけるトラブルと原因対策
・フライス用 SD,SE,TE 形標準インサートの各社形番対照表
・フライス加工の各社材種対応表
・旋削工具各部の名称と刃先角度の役割
・旋削用インサート形状と使用用途
・旋削の切りくず処理
・旋削に関する計算式
・旋削における工具損傷対策
・旋削における各要因の切削性能への影響
・旋削の各社インサートブレーカ対応表
・旋削の各社材種対応表
・ドリル各部の名称と働き
・タップ下穴に相当するドリル径
・ドリル加工計算式
・ドリル加工のトラブルと原因対策
・穴の公差等級並びに寸法許容差
・ねじの寸法規格
・工具鋼のブランド対照表
・表面粗さ
・被削性指数
・硬さ換算表
◆詳細はカタログをダウンロードしご覧いただくか、お気軽にお問い合わせ下さい。
このカタログについて
| ドキュメント名 | 切削工具 商品 技術資料 カタログ 2023~2024 |
|---|---|
| ドキュメント種別 | 製品カタログ |
| ファイルサイズ | 2.9Mb |
| 登録カテゴリ | |
| 取り扱い企業 | 株式会社MOLDINO (この企業の取り扱いカタログ一覧) |
この企業の関連カタログ

このカタログの内容
Page1
CUTTING TOOLS
PRODUCTS CATALOGUE
切削工具 商品カタログ
2023~2024
技術資料
Page2
技
技術資料 術
資
Technical Data 料
エンドミル各部の名称とエンド外径について……………I2
Name of parts for end mills and shapes of end cutting edges
エ エンドミルの刃形と切削性 ………………………………I4
Flute shape and cutting ability of end mills
ン
ド エンドミルの切削条件の求め方 …………………………I5
ミ How to determine cutting conditions of end mills
ル エンドミル使用上のご注意 ………………………………I6
Precautions in handling an end mill
エンドミル加工のトラブルと原因対策 …………………I7
Trouble shooting for end milling
フライス工具の各部の名称と刃先角度の役割 …………I9
Names of parts and roles for milling tools
刃 フライス用インサート各部の名称と役割 ……………I12
Names of parts and roles for milling inserts
先
交 フライス加工切削条件の選び方 ………………………I14
換 How to select cutting conditions for milling
式 フライス加工におけるトラブルと原因対策……………I15
工 Cutting condition formula (milling) and trouble shooting
具 フライス用SD,SE,TE形標準インサートの各社形番対照表 …I16
Comparison of inserts for milling SD,SE,TE type
フライス加工の各社材種対応表 ………………………I17
Table of corresponding materials from various companies for milling
旋削工具各部の名称と刃先角度の役割 ………………I19
Nomenclature of turning tools parts and role of nose angle
旋削用インサート形状と使用用途 ……………………I20
Shapes of inserts and application of turning
旋削の切りくず処理 ……………………………………I21
Chips removal of turning
旋 旋削に関する計算式 ……………………………………I22
削 Cutting condition formula for turning
工 旋削における工具損傷対策 ……………………………I23
具 Counter-measures against brakage of tools
旋削における各要因の切削性能への影響 ……………I24
Relashionship between cutting elements and cutting performance in turning
旋削の各社インサートブレーカ対応表 ………………I25
Comparison against competitor's insert breakers of turning
旋削の各社材種対応表…………………………………I26
Table of corresponding materials from various companies for turning
ドリル各部の名称と働き ………………………………I27
Name and function of each part of a drill
ド タップ下穴に相当するドリル径 …………………………I28
リ Drill dia. equivalent to a hole size before tapping
ル ドリル加工計算式 ………………………………………I28
Drilling work equations
ドリル加工のトラブルと原因対策………………………I29
Trouble shooting of drilling work
穴の公差等級並びに寸法許容差 ………………………I31
Standard tolerance grades and limit deviations for holes
ねじの寸法規格…………………………………………I32
Dimension standard for screw threads
参 工具鋼のブランド対照表 ………………………………I37
考 Table of corresponding Tool Steels brands
資 表面粗さ…………………………………………………I41
料 Surface roughness
被削性指数………………………………………………I42
Machinability indices
硬さ換算表………………………………………………I43
Hardness conversion table
I1
Reference data Drills Turning Tools Indexable Tools End Mills
Technical Data
Page3
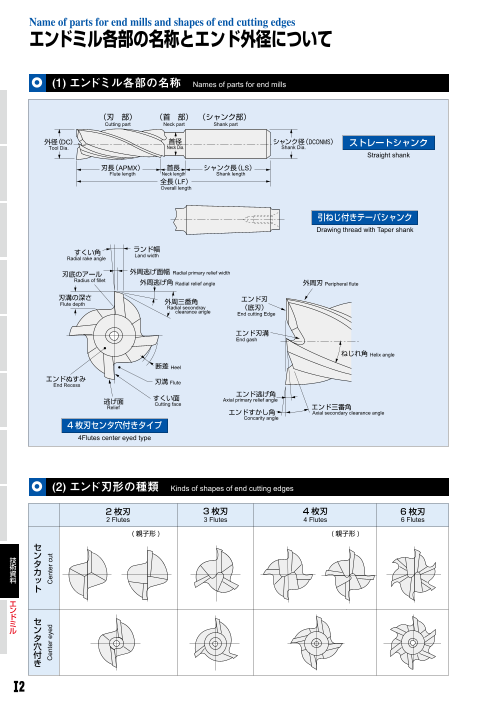
Name of parts for end mills and shapes of end cutting edges
エンドミル各部の名称とエンド外径について
(1) エンドミル各部の名称 Names of parts for end mills
(刃 部) (首 部) (シャンク部)
Cutting part Neck part Shank part
外径(DC) 首径 シャンク径(DCONMS) ストレートシャンク
Tool Dia. Neck Dia. Shank Dia.
Straight shank
刃長(APM((
(
((X刃
刃刃
刃)刃Cu
ttin部
部部
g部部 pa)
)) ((首首 部部)) ((シシャャンンクク部部))
CCuuttttiinngg ppaar)rrttt)首長 (((首首首NNe eec cckシkk 部 p部pp部aaャarrrt)tt))ンク(((長シ(シシLャャSャSSShhhaン)ンaanンnnkkk ク ク pppクaaarrrt部部tt部)
Flute lengthCutting part Neck length Neck part Shank lengtShhank part ))CCuuttttiinngg ppaarrtt NNeecckk ppaarrtt SShhaannkk ppaarrtt
CCuutttitningg p paartrt全長(LF)NNeecckk p paartrt SShhaannkk p paartrt
刃刃刃径径((DD)) Overall length 首首径径 シシャャンンクク径径((dd))
刃刃刃径M
M径(iili(
llll
l D
D
DDi
iaai)a.
.
.) 首NNN首eeeccc径kkk 径D DDiiaiaa... シシャャSンSShhンhaaaクnnnkクkk D 径DD径i(iaiaa.(.. dd))
M径M径illi l(Dl DD
iai.a.) NeN
首
cekc kD 径iDa.ia. シャ
ShSah
ン
nakn k
ク
D D
径
iai.a
(. d)
MM(ill liD lDl Diaiai)
. .a. 首
NNece
N
kc
e径
k
c
D D
k
iai
D
.a.ia. シャン
SShhSaahnna
ク
kkn D
k径D D(
iaia
i
. .ad.
d)
Mil
刃刃刃F 長長((
刃 s
刃F刃ll長uu長t長t長(e
e(l( (eleR n
R R )) 首首長長 シシャャンンクク長長((
R nR
g
g tt)hh)))
NN首eec首首c首kk長 lle長長e長nnggtthh シシシシャ
ャ
ャャン
SSンンン
hhクaanククnクkk長 l長le長長(e
nn(((
ggR tR
R
th
ss))
Flute length Neck length Shank lengtR hRh sss)) 引ねじ付きテーパシャンク
FlFFultlueut telee lnleegnntghgtthh N NeNceekcc klke lnleegnntghgtthh ShSSahhnaaknn klke lnleegnntgh
Flute length Nec全全k le長長ng((th LLL)) gtth
)
hss)
Flute length Neck length SShhaannkk l elennggthth Drawing thread with Taper shank
OOO全vv全全v全eeer長rara長長al長(lll l( (l( leleeLnnnLLLgLg)gtth)thh
Overall lengt)
)
Overall lenghth
OOO
vveevrar
earlll
a
ll
l
el
le lnneggntht
ghth
すくい角 ランド幅
Radial rake angle Land width
刃底のアール 外周逃げ面幅 Radial primary relief width
Radius of fillet 外周逃げ角 Radial relief angle 外周刃 Peripheral flute
刃溝の深さ ランド幅
Radす
す
すialく
く
くrakい
い
eい a角
角 ラランンドド幅幅
Radすialく rakいe a角n角gle ララLLンan
aンd
ndド w ドi
w幅did幅thth 刃
Flute depth
RRaaddiすiaall rくraakkeいe ananng角gle
L
le 外ラan周d w三idt番h 角 エンド
Radial rake anglgele LLaRnaadn
ン
ddw iaw
ド
idli tdsht
幅
ehcondray (底刃)
RRR
aadda
す
iai
dai
l l
aく
r ar
la rkka
い
eek a
ea 角
ランド幅
nnaggnlel
gele LLaaLn nd d
n
w
d
w
w
cildied
i
taht
dhth
rance angle
周逃げ面幅 RRaaddiaial lp prrimimaarryy r re
E
eli
n
le
d
ieff
wcu
widttidt
ihng Edge
刃刃 th
刃底底底Rの
の
のadア
ア
iアusー
ー
ーof ル
ル 外外周周逃逃げげ面面幅幅 Radial primary relief width
刃底のRaアdiuーs oルfルillet 外外周周逃逃げげ面面幅幅RRadaidaila pl rpirmimarayr yr erleielife fw widitdhth刃底Radius of ff iflilleltet 外外周周逃逃げげ角角RRR
aaddai idaila pl rpimrimarayr yre rleielife wf widitdhth
刃底RのR
の
adaidアui
ア
su soー fo
ー
ffル
外周逃げ面幅
iflli
ル 外周逃げ面幅
elltet 外周逃げ角 RRalad dpiairali mlr reaelrilyeief rf ae anlnigeglfel ewidth RRaaddiaial lF Flulutete
RRR
aaddaiui
dui
s s
u
o o
s
f f
o
f if
f
li
ll
f
el
iellt tet 外外外外周
周
周周逃
逃
逃逃げ
げ
げげ角
角Radial relief an
角角 Radial relief anエgglleeンド刃溝 外外外周周刃刃
RRR
aaddaiai
dai
l l
a
r er
le rlil
e
eie
li
f f
e
a a
f
nnaggnlel
gele 外外外周
周
周周刃
刃Radial Flute
Radial relief angle 刃刃RRadaidaila Fl lFultuete
End gash RRR
aaddaiai
dai
l l
a
F F
l
lul
Ful
tet
uete
刃刃刃溝溝のの深深ささ
刃刃刃
C
C溝
u溝t
溝u溝
ti
ttの
nのg
のinの
g深
d深e
深 d深
p
eさthさpさtさh 外外外周周周三三三番番番角角角 エエエンンンドドド刃刃刃
CCuuttttiinngg ddeepptthCutting depthh 外外外RR周Raad周adidi三aaila三l sls 番esec番ecoco角on角nddraray エエンンドド刃刃
ndrayy
CCututitntign gd edpetphth 外 R (((底底底刃刃刃))) ねじれ角
Cutting depth R aR 周 da
周
a id
ca cd il三icale ealsl
三
al
ae sra
r
s番caeareonc
番
ancnoc
c
o角
エンド刃
dence
角 エンド刃
rde aa rnyanagnyglgleele E(n(d底 c底ut刃ti刃ng) )Edge Helix angle
R R a ad d i ca i lace lsa esraecarconaoncnndecd re
nar dnya
rgynalgy clearance aneglle EEndn( dc uc底tutitnt刃ign gE) Edge
e E(nd 底cut刃ting)dge
断差 Heel c cleleaararannccee a anngglele End cutting E Edgdege
EEnnEddn c
dc
uucttt
u
itni
tntiggn E
gE
ddEggdeege
エンドぬすみ エエエEエンンンドドド刃刃刃溝溝溝
End Recess 刃溝 Flute エエEエnE
nンdndンン ンd ggド agasドashhs刃h刃溝溝
EEndn dg agド
ド
sahsh刃刃溝溝
エンド逃げEEnnEd角dn g dg
aagshs
ahsh
逃げ面 すくい面 Axial primary relief angle ねねじじれれ角角 HHeelilxix a anngglele
Cutting face ねじれ角Helix angle
Relief エンド三番角 ねねねじじじれれれ角角角HHeleixli xa nagnlgele
断断断差差差 Helix angle
HHHeeeeell
HHeleixli xa nagnlgele
断 el エンドすかし角 Axial secondary clearance angle
断断断差
差
差差HHeeelel
HHH
eeeeel lel Concarity angle
4 エエエンンドドぬぬすすみみ
エ枚エエン
刃ンEnドdドセ Rぬeぬンcすesすsタみみ穴付きタイプ 刃刃刃溝溝溝CChhipip s pspacae
ンE ce
EンnEnドdnd ドd RRぬ eReぬcceeすecssesすsssみみ 刃刃
4 刃溝溝
Chip space
End Recess 溝CChihpi ps psapcaece
EFEnnEdludn R tdR R
eeecsceeecs sscessesnter eyed type 刃溝CCC
hhipi
hpi
s
p
psp saapccaeece
Axial エ
エ
pエrエimン
ン
ンaンrド
ド
yド ドre逃
逃
逃li逃efげ
げ
げ aげn角
角
g角l角e
逃逃逃逃げ
げ
げげ面
面 すすくくいい面面
面 すくい面 AxAixali apl rpimrimarayr yre rlieelfie afn agnlgele
面面 すすCCくuuCtくtuttitiいntnigいgn gf面f a面fcae
エンド逃げ角
逃Rげelief acece AAxixaila plエ rpエirmiンmンarayドr yドr erl逃eiel逃ife げfa げnagn角lg角Axial primary relief ane
ReRlieelfief Cutting face glle逃げ面 すCutくtingい fa面ce e
逃Rげeli面
す
ef Cくuttいing 面face AAxxiaial lp prirmimaaryry r erelileief fa anngglele エエエンンンドドド三三三番番番角角角
ReRlieelfief CCuutttitningg f afaccee エエエンンンドドドすすすかかかししし角角角 エAエAxAンxiンixaalilド a sslドe esc三ceooc三nnod番dna番adrray角yr 角yccl lecealaerraaarnnaccneec aean naggnllgeeRelief le
Relief エエンンドドCCすoConすnoccnかaacかrraiitしrtyiyしt aya角n nag角gnllgeele エAAエxiンxaiンla slド esドceoc三no三dna番dra番yr y角c 角lcelaeraarnacnec ea nagnlgeleエエンンドドCCoすnoすcnacかraかirtyitし yしa na角gnlg
角
ele AAA
xxiai
xai
l l
a
s es
le scceoocnnoddnaadryr
ayr c
yc
lel
cel
aaerar
aarnnaccneec a
ea
nnaggnlel
gele
CCC
oonnoccnaacrir
a
tiyt
ryit a
ya
nnaggnlel
gele
(2) エンド刃形の種類 Kinds of shapes of end cutting edges
2 枚刃 3 枚刃 4 枚刃 6 枚刃
2 Flutes 3 Flutes 4 Flutes 6 Flutes
( 親子形 ) ( 親子形 )
セ
技 ン
術 タ
資 カ
料 ッ
ト
エ
ン
ド
ミ セ
ル ン
タ
穴
付
き
I2
Center eyed Center cut
Page4
(3)エンドミル刃部の形状 Shape of end mills flute
スケアエンド ラジアスエンド ボールエンド
Square end Radius end Ball end
テーパ刃スケアエンド テーパ刃ラジアスエンド テーパ刃ボールエンド 総形エンド
Tapered cutting part with square end Tapered cutting part with radius end Tapered cutting part with ball end Formed end
(4)シャンクの種類 Kind of end mill shank
シャンクの種類 名称・特徴 シャンクの種類 名称・特徴
ストレートシャンク コンビネーションシャンク
(プレーンシャンク) (ダイナシャンク)
Straight shank Combination shank
(Plain shank) (Dyna shank)
・大径シャンク用。
・国内ではφ 50.8 が普及。
・通常φ6〜φ42で使用される。 ・For shanks with a large diameter
・Shanks of φ6 to φ42 are usually used. ・A shank of φ50.8 is popular in Japan.
フラット付きストレートシャンク 引きねじ付きテーパシャンク
(サイドロックシャンク) Taper shank with drawing screw
(ウエルドンシャンク)
Straight shank with flat (side lock shank)
(Weldon shank)
・米国普及品。
・φ 20 以上はダブルフラット付き ・モールステーパB&Sテーパが
・Popular in U.S.A. ある
・Products of φ 20 or larger have double ・Available with Morse taper and B&S
flats. taper
傾斜フラット付き BT シャンク
ストレートシャンク BT shank
Straight shank with sloped flat
Straight shank
・マシニングセンタ用
・軸方向調整機能付き ・ATC 用
・With axial adjusting function ・For a machining center
・For ATC
ねじ付きストレートシャンク 7/24 テーパシャンク
Straight shank with screw (ナショナルテーパシャンク)
7/24 taper shank
(National taper shank)
・欧州普及品 ・機械直付け用
・Popular in Europe ・Directly attached to a machine.
・フラット、外ねじの寸法はご指定のない場合は、当社規定によります。引きねじはミリ、インチをご指定ください。
Dimension of flat and outside screw, if not specified, should be in accordance with the stipulations. Please specify dimension of drawing screw
in mm or inch.
I3
Technical Data End Mills
Page5
Flute shape and cutting ability of end mills
エンドミルの刃形と切削性
(1)外径DC と刃長 ℓ (2)ねじれ角について
Mill diameter (DC) and flute length (ℓ) Helix angle
切削工具の切削性は、シャープな切れ刃と刃部の剛性とから得 通常、エンドミルのねじれ角は、右ねじれ 30°前後で製作さ
られますが、エンドミルではとくに剛性が重要な因子となります。 れています。ねじれ角は次のような機能があります。
剛性が低いと切削中にエンドミルがたわんで振動が生じます。そ ① 切削抵抗の断続的な変動を緩和し、振動をやわらげ工具寿命を
の結果加工精度を悪くし、エンドミルの摩耗を早めますので、切 延ばします。
削条件を最大限に生かせません。 ② 被削材へのくい付きがよくなり、切削力が減少します。
エンドミルの剛性は、外径DC と刃長 APMX で決まると考えて ③ 切りくずを軸方向に排出し、切削面への切りくずのかみ込みを
よく、たわみについては概略 なくします。
Cutting ability of cutting tools depends on sharpness of cutting edges and しかし、ねじれ角が大きい場合は、軸方向に切削力がかかるので
stiffness of cutting part. Particularly, stiffness is a significant factor in using 工具の保持を強固にしなければなりません。また、工具剛性や主
an end mill. Low stiffness may cause vibration during cutting work due to a
deflected end mill, resulting in poor machining precision and early wear of 軸クリアランスの関係で切削面がわずかに傾くことに注意が必要
end mills. Therefore, low stiffness will not allow cutting conditions to be です。
exploited to the full stiffness of an end mill is determined by the mill 当社では、工具剛性を大きくできる場合に45°〜60°ねじれを
diameter, DC, and the flute length, ℓ. Deflection is practically given by the
following formula : 製品化しています。また、加工精度の厳しいキー溝用エンドミル
は、12°ねじれを採用しております。
δ= C APMX3 End mills usually adopt right-hand helix angle of approximately 30°. Helix
DC4 angle has the following effects :
① Helix angle relieves intermittent fluctuation of cutting resistance, lightens
ただし、δ:たわみ vibration, and prolongs cutting life of tools.
C:定数 ② Helix angle enables smooth bite into work material, and reduces
necessary cutting force.
where T is deflection and C is constant. ③ Helix angle allows chips to be discharged in axial direction, and
becomes free from jamming of chips.
a b In the case of high helix angle, however, a tool must be held securely since
cutting force is applied in the axial direction. Besides, care must be taken
の関係があります。つまり計算上は刃長が 25%長くなるとたわ on the surface to be cut which is slightly inclined due to the relation
みは2倍に大きくなり、外径が20%太くなると半分に減少します。 between tool stiffness and clearance of main spindle. Manufactures end
mills with high helix angle of 45 °to 60 °at which high stiffness of tool is
また、工具寿命への影響も下図より明らかで、加工部位の形状に secured. As for key-way end mills for which strict machining precision is
よりますが、能率切削のためには、できるだけ剛性の大きい工具 required, 12 ゜of helix angle is adopted.
が推奨されます。ロングシャンクエンドミルは、ロング刃長のエ
ンドミルよりも刃長をおさえ、剛性の大きいシャンク部を長くし
てあり、深彫加工に適します。
In brief, deflection increases twice if the flute length increases by 25%, or
itdecreases one-half if the mill diametear increases by 2b0%. The following
shows the effect of flute length on cutting life of tools,indicating that it is
recommended to use a tool with as high stiffness as possible to obtain high
efficiency cutting. The long shank type end mill has short flute length and
long shank with high stiffness compared with the long flute length type, and
is suited to deep contouring. a b
時間
( mm ) Time
4,000 a:最大切削力
Max. cutting force
2,500
4NKS10 φ10×18ℓ b:切削力の変動
1,600 4NKR10 φ10×25ℓ Fluctuate of cutting force
4NKLE10 φ10×45ℓ
1,000 4NK×10×60 φ10×60ℓ
工 4NK×10×80 φ10×80ℓ a b
具 630 回 転 数 n=655min-1
寿 切 削 速 度 vc=20.6m/min
命 400
( テーブル送り vf=62mm/min
L 1 刃 当 り fz=0.047mm/t 時間
) 250 切込深さ×幅 ap× ae=4.5 × 9mm Time
技 被 削 材 DM(31HRC)Dry
術 160 ℓ
資
料 100
DC
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 ( mm )
刃長(R ) ( mm )
エ 4,000
ン 刃長と工具寿命
ド 2,500
ミ Flute length and Tool life
1,600
ル
1,000
工
具 630
寿
命 400
(
L
) 250
I4 160
R
100
Dc
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
刃長( mm
R ) ( )
刃長と工具寿命
切削力 切削力
Cutting force Cutting force
Page6
How to determine cutting conditions of end mills
エンドミルの切削条件の求め方
(1)切削速度 (vc) と回転数 (n) (3)切込み (ap×ae) Depth of cut (ap×ae)
Cutting speed (vc) and revolution number (n) 切り込み量は、取り代の大きさで決まります。加工目的に合わせて、
回転数 (n) は、切削速度と使用する工具の外径から次式により計 推奨条件の切り込み量を参考にしてください。
算します。ただし、ボールエンドミルでボール刃部分のみで切削 Depth of cut (ap×ae) is basically determined by the size of machining allowance.
する場合は、実質的な工具外径は切削部分の最大径となります。 Please refer each item recommend cutting condition to match cutting purpose.
計算の際は DC を切削状況に合わせ、小さく設定してください。
The revolution number (n) is calculated by the following formula using cutting
speed and flute length of the tool to be used. When cutting work is performed by
using only a ball end cutting part of a ball end mill, however, select a tool with the
substantial flute length equal to the maximum diameter of the portion to be cut. (4)切りくず排出量(Q) Chip removal volume (Q)
In calculation, set DC to a smaller value according to the cutting condition.
n = 1000×vc
π× DC (min-1) Q=—ap× ae× v f
1000 (cm3/min)
Q : 切りくず排出量 cm3/min ae: 切削幅 ㎜
n:回転数 min-1 DC:外 径 ㎜ Chip removal volume Cutting width
Revolution, min-1 Tool diameter, mm ap: 切込み深さ ㎜ v f: 1分間当りのテーブル送り速度 ㎜/min
Cutting depth Feed rate per minute of table
vc:切削速度 m/min π:円周率(3.14)
Cutting speed, m/min. Ratio of circumference of a
circle to its diameter (3.14)
外径
DC
DC´実質的な外径 Substantial tool dia.
(2)送り速度(v f) と1刃当たり送り(fz)
Feed speed (v f) and feed per tooth (fz)
作業能率は、テーブルの送り速度(v f)で決まりますが、切削条件は
1刃当り送り(fz)をさきに定めます。ほかの条件は工具の大きさ(外
径と刃長)、刃数、被削材の被削性、加工精度、機械容量などを考
慮して決定します。
Working efficiency is determined by the table speed (v f), but the feed per tooth should
be fixed first of all in setting cutting conditions. Other conditions should be determined
considering dimension of a tool (mill diameter and flute length), number of flutes, work
ability of work material to be used, machining precision, and capacity of a machine to
be used.
送り速度は、1刃当り送りから次式で計算します。
v f = fz× z× n (mm/min)
v f:送り速度㎜ /min z:刃 数
Feed speed, mm/min. Number of flutes
fz:1 刃当り送り㎜ /t n:回転数 min-1
Feed/tooth, mm/tooth Revolution, min. -1
(5)ボールエンドミルのピックフィードと理論カスプハイト表(μm) Ball end mill pick feed and theoretical cusp height table (μm)
ピックフィード量:ae (mm) Pick Feed ピックフィードとカスプハイト
0.05 0.075 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 Pick Feed and Cusp Height
0.5 0.63 1.41 2.51 5.66 10.10 23.03 41.74 66.99 H=RE- RE2-ae2/4≒a 2
e /8RE
1.0 0.31 0.70 1.25 2.82 5.01 11.31 20.20 31.75
2.0 0.16 0.35 0.63 1.41 2.50 5.63 10.03 15.69
ボール半径RE 3.0 0.10 0.23 0.42 0.94 1.67 3.75 6.67 10.43 RE
Ball Radius 4.0 0.08 0.18 0.31 0.70 1.25 2.81 5.00 7.82
(mm) 5.0 0.06 0.14 0.25 0.56 1.00 2.25 4.00 6.25
6.0 0.05 0.12 0.21 0.47 0.83 1.88 3.33 5.21 H
8.0 0.04 0.09 0.16 0.35 0.63 1.41 2.50 3.91
10.0 0.03 0.07 0.13 0.28 0.50 1.13 2.00 3.13 ae
I5
Technical Data End Mills
Page7
Precautions in handling an end mill
エンドミル使用上のご注意
(1)機械 Machine (4)作業 Work
・ 加工物の大きさに見合った機械を選んでください。加工精度と ・ 切削条件は加工物や作業条件で激しく変化しますが、標準条件
加工能率を得るのに必要な動力と機械剛性を有していることが 表を参考にして、適宜増減してください。
重要です。 ・ ホルダやエンドミルのオーバハングは可能な限り短かくしてご
・ 使用するエンドミルに適する回転数や送り速度が選べることを 使用ください。ドゥエリング(静止位置回転)は逃げ面摩耗を
確認してください。 早めますのでなるべくお避けください。
・Select a machine consistent with the size of work piece to be ・ できるだけ切削油をご使用ください。
used. It is important that the machine has enough power and
mechanical stiffness to achieve necessary machining 切削個所へ十分な量を供給してください。
precision and machining efficiency. また、切込みの大きい場合は切りくず排除の目的で高圧で切削
・ Check whether you can set the machine to the revolution number and feed 油、ミストまたはエアを供給することをお推めします。
speed suitable for the end mill to be used.
・ エンドミルの再研削は下表を参考にして、早や目に行ってくだ
さい。摩耗幅が限度を超えると急速に摩耗が進行し、再生でき
(2)ツーリング Tooling ないことがあります。
・ エンドミルホルダは、精度と把握力が十分なものを使用してく ・ 超硬エンドミルの場合は、ハイスエンドミルの 50%〜 60%
ださい。とくに小径エンドミルでは振れが、大径やラフィング を目安にしてください。一般に未使用品に比べ再研削に時間を
刃では把握力が大切です。 要します。過大摩耗はチッピングの原因にもなりますのでご注
意ください。
・ 加工物の固定を確実にしてください。強ねじれ刃を使用の場合
・ Cutting conditions vary with the kind of work piece and change of working
や重切削の場合は、ワークのがたつきや工具の抜け出しにご注 conditions. Refer to the table of standard conditions to select proper conditions.
意ください。 ・ The overhang of the holder or the end mill should be as short as possible.
・ Use an end mill holder with sufficient precision and grasping force. In using an ・Avoid dwelling because it may hasten wear of flanks.
end mill with a small mill diameter, select an end mill holder mainly considering ・It is better to use cutting fluid, if possible.
deflection. When using an end mill with a large mill diameter or a roughing type
end mill, it is important for an end mill holder to have sufficient grasping force. ・Apply a sufficient amount of cutting fluid to the place to be cut.
・ Fix the work piece securely. When using an end mill with high helix angle or In the case of large depth of cut, it is recommended to supply cutting fluid, mist,
when performing heavy duty cutting, be careful about shaking of the work piece or air to the place at high pressure during cutting in order to discharge chips.
and slipping of the tool. ・ Perform re-grinding of a worn-out end mill as early as possible after referring to
the following table. There may be cases where, if depth of wear exceeds the
limit, wear may proceed so rapidly that re-grinding may become impossible for
(3)エンドミルの選択 Selection of an end mill re-utilization.
・ As for carbide end mills, re-grind them when the depth of wear reaches 50% to
・ 作業目的に合ったエンドミルをご使用ください。疑問のある場 60% of the limit value of high speed steel end mills. Generally, it takes more
time to re-grind the worn end mill than an unused one.
合は、当社へご相談ください。
Be careful of excessive abrasion because it may cause chipping.
・ 切削性本位には大径でショート刃形状とし、工具剛性の大きな
ものが推奨されますが、テーブルの送り速度は 1 刃当りの送り
との関係で外径15〜25㎜付近が最も大きくできます。取り代
と併せてご検討ください。
・Be sure to use an end mill matching the working purpose. If you have any
question, please make contact with us.
・ It is recommended to use a short flute length type end mill with a large mill
diameter and tool stiffness, when you consider cutting ability first. To obtain the
maximum feed speed of the table, use an end mill with approximately 15 to 25
mm of mill diameter, because the feed speed is dependent on the feed per
tooth. Carry out a detailed study in selecting an end mill in addition to
allowance.
表 3 逃げ面摩耗幅による再研削時期の判定 Judgment of re-grinding time based on depth of wear on a flank 単位㎜
仕上げ用 荒加工用 ラフィング刃
Finishing Roughing Roughing flute
外径10以下 0.1 〜 0.15 0.15 〜 0.2 _
Tool Dia.under 10
ハイス 外径10〜30
High speed steel Tool Dia.10~30 0.15 〜 0.2 0.2 〜 0.3 0.3 〜 0.5
外径30以上
Tool Dia.over 30 0.2 〜 0.3 0.3 〜 0.5 0.5 〜 0.7
技
術
資
料
標準切削条件の選定 Selection of standard cutting conditions
エ 新しい作業の立上げの目安としてご利用ください。最適切削条件は上述のご注意のほか、種々の要因があります。
ン
ド Use them as a guide in starting a new work. To select the optimum cutting conditions, take various factors into consideration in addition to the cautions described above :
ミ ・被削材が硬目の場合や切込みが大きい場合やロング刃長を使用の場合は、回転数を低めに設定してください。
ル ・寸法精度や仕上げ面粗さが重要な場合や機械出力の小さい場合は、送り速度を低くしてください。
・精度重視の作業には、一般に多刃エンドミルが適当です。
・ When using hard work material, in the case of large depth of cut, or when using an end mill with long flute length, set the revolution number to the lower value.
・ If high dimensional precision or excellent roughness of finished surface is significantly required, or when output of a machine to be used is low, set the feed
speed to the lower value.
・Multi-flute end mills are generally suitable for cutting works requiring high precision.
I6
Page8
Trouble shooting for end milling
エンドミル加工のトラブルと原因対策
ト ラ ブ ル 現 象 原 因 対 策
・外周逃げ角、すくい角が大きく、切れ ・逃げ角、すくい角を適正にする。
刃角が小さい。
切 削 中 の び び り ・ワークの取付けがよくない。 ・ワークを強固にとりつける。
・機械、チャックの剛性不足。 ・機械、チャックの交換。
・切削速度、送り速度が速い。 ・切削条件を変更する。
・エンドミルの腰が弱い。 ・剛性設計の工具を使用する。
・送り速度が速い。 ・送り速度を遅くする。
・切込みが大きい。 ・切込みを少なくする。
切 削 中 の 折 損
・突き出し量が長い。 ・突き出し長さを短くする。
・切れ刃が摩耗している。 ・早期に再研削する。
・必要以上に刃長が長い。 ・短い刃長のものにとりかえる。
・ワークの固定が弱い。 ・ワークを強固に固定する。
・送り速度が速い。 ・送り速度を下げる。
・刃先角が小さい。 ・角度を適正に研削する。
切 削 中 の 刃 か け
・チャックの締付け不足。 ・工具のチャッキングを確実にする。
・切込みが大きい。 ・切込みを少なくする。
・機械の剛性不足。 ・機械を変更にする。
・切削速度が速い。 ・切削速度を遅くする。
摩耗、焼けが著しい ・外周逃げ角が小さい。 ・適正逃げ角に修正する。
・被削材硬さが高い。 ・工具に表面処理を行う。
・切れ刃の摩耗が大きい。 ・再研削を行う。
切 れ 味 が 悪 い ・被削材と工具の不適性。 ・専用工具を使用する。
・すくい角が小さい。 ・適正すくい角に修正する。
・切削量が大きすぎる。 ・送り速度、切込み量を調整する。
・チップポケットが小さい。 ・刃数の少ないエンドミルを使う。
切 れ く ず づ ま り
・切削油が少ない。 ・切削油を多量にかける。
・チップポケットの形状が悪い。 ・適正形状に修正する。
・外周逃げ面摩耗が大きい。 ・早期に再研削する。
仕 上 面 の か え り ・切削条件の選定ミス。 ・切削条件を見直す。
・外周逃げ角、すくい角が不適性。 ・適正な角度に修正する。
・送り速度が速い。 ・送り速度を下げる。
・切削速度が遅い。 ・回転を上げる。
仕上面粗さが悪い ・切れ刃の摩耗が大きい。 ・再研削する。
・切りくずのかみ込み。 ・切込みを小さくする。
・エンド刃の中低勾配が小さい。 ・中低勾配を大きくする。
・送り速度が速い。 ・送り速度を下げる。
・ねじれ角が大きい。 ・ねじれ角の弱いものを使用する。
切 削 溝 の た お れ
・オーバハングが長い。 ・突き出し長さを短くする。
・切込みが大きい。 ・切込みを小さくする。
・機械、チャックの精度不良。 ・機械、チャックを修理する。
寸 法 精 度 が 悪 い ・刃長が長い。 ・適正刃長のものを使用する。
・機械、チャックの剛性不足。 ・機械、チャック変更する。
I7
Technical Data End Mills
Page9
Trouble shooting for end milling
エンドミル加工のトラブルと原因対策
Symptoms of troubles Probable causes Remedies
・Low-angled cutting edge due to too high ・Mend the flank angle and rake angle
peripheral flank angle and rake angle properly.
Chatter during cutting ・The work piece is not attached securely. ・Fix the work piece firmly.
・Insufficient stiffness of machine and ・Replace the machine and chuck with
chuck. properones.
・Too high cutting speed and feed speed. ・Change cutting conditions.
・The end mill lacks firmness. ・Use a tool designed to have high
stiffness.
・Too high feed speed. ・Decrease the feed rate.
Breakage during cutting ・Too large depth of cut. ・Make small depth of cut.
・Excessively long protrusion. ・Shorten the protrusion length.
・Worn-out cutting edge. ・Perform re-grinding in early stage of wear.
・The flute is longer than it need to be. ・Replace the end mill with a new one
having shorter flute length.
・The work piece is not fixed firmly. ・Fix a work piece firmly.
・Too high feed speed. ・Decrease the feed rate.
Broken cutting edge during cutting ・Low-angled cutting edge. ・Grind the angle properly.
・Lack in tightening of chuck. ・Perform chucking of a tool reliably.
・Too large depth of cut. ・Make small depth of cut.
・Insufficient stiffness of machine. ・Replace the machine with a proper one.
・Too high cutting speed. ・Slow down the revolution number.
・Excessively small peripheral flank angle. ・Modify the flank angle properly.
Serious wear and burning ・Hardness of the work material is too ・Apply surface treatment to a tool to be used.
high.
・Excessively worn-out cutting edge. ・Perform re-grinding.
Poor cutting quality ・A tool to be used is not suited to the work ・Use a tool specially designed for the work.
material.
・Too small rake angle. ・Modify the rake angle properly.
・Too large amount of chips are produced. ・Adjust the feed speed and depth of cut.
・Small chip pocket. ・Use an end mill having less number of flutes.
Chip clogging ・Insufficient application of cutting fluid. ・Apply a large amount of cutting fluid to
work mateial.
・Improper shape of chip pocket. ・Modify the chip pocket to have a proper shape.
・Seriously worn-out peripheral flank. ・Perform re-grinding in early stage of wear.
Burr on the finished surface ・Mistake in selection of cutting conditions. ・Re-examine cutting conditions.
・Improper peripheral flank angle and ・Modify the angle properly.
rake angle.
・Too high feed speed. ・Decrease the feed rate.
・Too slow cutting speed. ・Increase the revolution number.
Insufficient roughness of ・Excessively worn-out cutting edge. ・Perform re-grinding.
finished surface ・Chips bite the work material. ・Make small depth of cut.
・Too small medium to low gradient of end ・Make the medium to low gradient greater.
技 cutting edges.
術
資
料
・Too high feed speed. ・Decrease the feed rate.
Inclination of slot ・Too large helix angle. ・Use and end mill with smaller helix angle.
エ ・Too long overhang. ・Shorten the protrusion length.
ン
ド ・Too large depth of cut. ・Make small depth of cut.
ミ
ル
・Insufficient precision of machine and chuck. ・Repair the machine and chuck.
Poor dimensional precision ・Too long flute length. ・Use an end mill with proper flute length.
・Insufficient stiffness of machine and chuck. ・Change the machine and chuck.
I8
Page10
Names of parts and roles for milling tools
フライス工具の各部の名称と刃先角度の役割
フライス工具各部の名称 Name of parts of milling tool body
穴径
Bore dia.
コーナ角 アキシャルレーキ
Corner angle (軸方向すくい角)
カッタ高さ (A.R.)
Height of cutter body Axial rake angle
(Rake in axial direction)
(A.R.)
切込み角
Approach angle
副切れ刃逃げ角
カッタ径(外径) Relief angle of axially cutting edge
Cutter dia.
切れ刃傾き角(1 )
真のすくい角(T) Angle of inclination of cutting edge(1 )
Orthognal rake
angle(T) ラジアルレーキ
(半径方向すくい角)
(R.R.)
Radial rake angle
(Rake in radius direction)
(R.R.)
主切れ刃逃げ角
Orthogonal cleanance angle
真のすくい角と切削性能 Relation between Orthognal Rake and Performance
真のすくい角 切れ味 切削動力 刃先強度 発熱 切りくず排出性 耐溶着性
Toughness of
True rake Sharpness Cutting power cutting edge Heating Chips ejectability Welding resistance
正(大) 良い 小さい 弱い 少ない 悪い。カッタ内にまき込む傾向ある 良い
Positive (large)
Good Small Weark Low Bad. May be caught by cutter. Good
負(小) 悪い 大きい 強い 多い 良い。カッタの外側に出る 悪い
Negative (small) Bad Large Strong High Good. Ejected outside the cutter. Bad
真のすくい角はカッタにセットするインサートの逃げ角によってほぼ決まり、インサートの逃げ角が強い程、真のすくい
角も強くなるように設定されています。
Effective rake angle is generally designed according to clerance of inserts used. The larger the clerance of an inserts is,the largr effective rake angle may be designed.
I9
Technical Data Indexable Tools
Page11
Names of parts and roles for milling tools
フライス工具の各部の名称と刃先角度の役割
カッタ径とエンゲージ角 Cutter dia. and engage angle
エンゲージ角が大きいと被削材食付時にインサート
の刃先より当たるため寿命が短くなります。 エンゲージ角(大)の場合 エンゲージ角(小)の場合
Higher engage angle Low engage angle
Lower engage angle shows short tool life, because engagment starts
from cutting edge of inserts in milling operation.
カカッッタタ中中心心 刃先刃か先らか当らた当るたる 奥の方奥かのら方当かたらる当たる
CCeeカnnteッtre orタ fo c中f uctu心tettrer StaSrtt刃 aartt 先 cautかt tcinuらgtt ie当ndggた eed る
奥の方から当たる
ogfe a on fi nasne irnt.sert. Start aStt ainrst iadte i nosf iadne inosf earnt. insert.
カeッntタer 中of c心u ter S刃Sttaa先rrtt aaかtt ccらuuttt当iinnggた eeddるggee ooff aann iinnsseerrtt
S奥Sttaaのrrtt aa方tt iinかnssiidらdee 当ooff aたann る iinnsseerrttCenter of cutter
Ceenntteerr ooff ccuuttteerr SSttaarrtt aatt ccuutttiinngg eeddggee ooff aann iinnsseerrtt SSttaarrtt aatt iinnssiiddee ooff aann iinnsseerrtt
インイサンーチサトッープト
カッタ中心 被削材刃先から当たる InseIrnt被削材 sert 奥の方から当たる
チIInnsッseerrプt被t 削被材削材
Center of cutter WoWrk被oSrkt削art材 at cutting edge of an insert. Start at inside of an insert.
IInnsseerrtWt orkW被ork削材
W被oo削rrkk材 W被oo削rrkk材 インサイーントサート
Woorrkk Woorrkk Insert Inチseッrtプ
エンゲージ角(大) インエサンートゲージ角(小)
HiエgHhンigehr
ゲ
eern
ー
geangジgea
角
ga
(
en gal
大e ) InseLrot wエ enンgaゲgeー anジgl角e(小)
ngle Low engage angle チIInnsッseerrプtt
被削エ材ンゲージ角(大) エンゲージ角(小)
WorkHiigghheerr eennggaaggee aann1ggl刃lee の送り Loo被w e削enngg材aaggee aannggllee IInnsseerrtt
エンゲージ角(大) エンWoゲrkージ角(小)
エンゲージ角(E) Fe1e
Hiigghheerr eennggaaggee aanngglleeFd
刃
1e rea
の
刃dte
送り
エ rのate送り Loow eennggaaggee aannggllee
エE
ンnンg
ゲaゲg
ーe ーa
ジnジg
角le(角 ((E
E))E) カッタ食付き部 1刃の送り インサート
Engage angle (E ) Sカ 1FFe刃eeeddの rraat送tee り 1刃のIn送seりrt
エEnnンggaagゲgee aーannggジllee 角 ((E()) E) Stta
ッ
カarrtッti
タning
食
タg p p食o
付
oini付nt
き to きof
部 1
fc uc部tutitg
Feed ra刃teの送り
tig Feed rate
エンゲージ角(大) FFeeeedd rraatエtee ンゲージ角(小)
Ennggaaggee aannggllee ((E)) SカSttaaッrrttiタinngg 食 ppoo付iinnttき ooff 部 ccuutttiigg Higher engage angle Low engage angle 1FFee刃eedd の rraat送tee り
SSttaarrttiinngg ppooiinntt ooff ccuutttiigg 1刃の送り FFeeeedd rraattee
エンゲージ角(E) Feed rate
Engage angle (E ) カッタ食付き部 (小) エンゲージ角(E) 1刃の送り (大)*
Starting point of cuttig Feed rate
Small Engage angle (E) Large
*カッタ径は被削材の幅より 30 〜 良 寿命 悪
Long Short
50%位大きめの径を使用した方が Tool life
良い結果が得られます。 カッタ径大 カッタ径小
Large cutter dia. Small cutter dia.
Cutter bodies are reccomend with diameter カ
30-50% biger than width of work pieces. ッ
タ
径
と
エ
ン
ゲ E
E
ー E
ジ E E
角 E E
E
E
E
カ
ッ
タ
位
置 E
と
エ E E
ン E
ゲ E
ーE E
E
ジ
角 E
E
技
術 カッタ大
資 Large cutter dia.
料 被削材 Work カッタ大
Laカrgッe タcu大tter dia.
Lカaarッrggeタe ccu大uttteerr ddiiaa
カッタ径が大きすぎるとカッタが被削材に食付
刃 カッタL大カッタ被移削動材距離W小ork aarrggee ccuuttteerr ddiiaa いて抜けるまでの距離が長くなり能率が低下し
先 被削材 Woorrkk Large cutter dia.
Short distance of moving of cutter
交 被削材 カッタ小
被削材 WorkWoorrkk ます。
換 Small cutter dia.
カッタ移動距離大小 Cutter with too large diamter shows lower machining
式 SLhoカongッrt dタiist移taann動ccee 距o of f離m mo小ovviningg o fo cf uctutettrer efficiency, bacause talking cutter path longer.
工 S カッタ小
具 カッカSタhhoッo移rrtタt d動dii移sst距taan動nc離cee距 小oof離f m小oovviinngg ooff ccuuttteerr Smカaッll タcu小tter dia.
SカhoSッSrhth タodorritst移 dtdaiisn動stctaaen距n ccoee離f omoff大 o mvoionvvgiin noggf ocofuf ctctueutrtteerr カッタSカS小mッaalタll ccu小uttteerr ddiiaa
Loカngッ dタist移an動ce距 of離 mo大ving of cutter Small cutter dia.
カッLタoonn移gg dd動iisst距taannc離cee o大off moovviinngg ooff ccuuttteerr SSmaalll ccuuttteerr ddiiaa
カッタ移動距離大
LonLgoo dnniggs t dadiinsstctaaenn coceef omoff o mvionovvgii nnoggf ocofuf tcctueutrtteerr
I10
Cutter position and engage angle. Cutter diamter and engage angle.
Page12
切込み角と切削性能 Relation ship between cutting edge angle and Performance.
切込み角90°
Cutting edge angle:90° 切込み角30°
Cutting edge angle:30°
fz fz
切りくず厚み≒1刃当たりの送り量(fz)
Chip thickness ≒ Feed rate per Tooth (fz) 切りくず厚み≒1刃当りの送り量の半分(—fz
2 =fz')
Chip thickness ≒ Feed rate per Tooth (fz/2 = fz′)
切りくず幅=切り込み量(ap) 切りくず幅=切り込み量の 2 倍(2ap)
Chip width = Depth of cut (ap) Chip width = 2 times the Depth of cut (2ap)
【注意】ただしアクシャルレーキを 0 と゚した場合
【Note】Based on 0 ゜axial rake
切込み角と切削性能の変化 Relation ship between cutting edge angle and performance.
大 切り込み角
切削性能要素 小
Large Cutting edge angle Small
Cutting performance factor 90° 75° 65° 45° 30°
切りくず形状 厚くて幅が狭い 薄くて幅が広い
Chips shape Thick and narrow Thin and broad
* 切りくず厚み比較 1 0.97 0.91 0.71 0.5
Comparison of chips thickness
切 削 動 力 少ない (ワークに接触する切れ刃長さによる) 大きい
Cutting power Small Depends on the cutting edge length that contacts. Large
インサート摩擦度 多い (切れ刃単位長さにかかる切りくず厚さによる) 少ない
Inserts abrasion Hight Depends on chips thickness per unit length of cutting edge. Low
び び り 出にくい (切れ刃長さによる食い付きの差) 出やすい
Vibration Not likely Depends on bite per unit length of cutting edge. Likely
有効切り込み深さ 大きい (インサートの倒れの差) 小さい
Effective depth of cut Large Inserts falling difference Small
振 動 出やすい (スピンドルに対して横からかかる負荷の差) 出にくい
Vibration Likely Differrence in the load that is applied transversely against the spindle. Not likely
ワークを下に押し付ける力 小さい (薄板では切込み角小さいとワークがビビル) 大きい
Work pressurizing force Small For thin plate, small cut-in angle causes work to chatter. Large
切りくずの流れ 良くない (横に巻込む) (上に出る) 良い
Chips flow No good Caught horizontally Ejected upward. good
*切込み角90°の時の切りくず厚みを 1 とした場合、同じ送りでの切りくず厚み比較。
* Comparison of chip thickness in various angles at a fixed feed rate (if 90°= 1 thick)
I11
ap
ap
Technical Data Indexable Tools
fź
Page13
Names of parts and roles for milling inserts
フライス用インサート各部の名称と役割
ホーニング (インサート)
ホHーonニingング (イン(Inサseーrtsト) )
ホHoーniニngング (チ(Inッseプrts))
Honing (Inserts)
ワイパー幅
コーナ高さ ワWイipパer ーwid幅th (被削材)
コCーornナer高 heさight ワWイipeパr wーid幅th (被Wo削rk材)
コーナー高さ Wiper width (
Corner height W被o削rk 材)
内接円寸法 Corner height Work
Inscribed circle dia. 外周切れ刃(主切れ刃)
内接円寸法
内Ins接cr円ibe寸d 法circle dia. 外Pe周rip切heれra刃l c(utt主ing切 edれge刃 )
外(M周a切in cれut刃tin(g e主dg切)れ刃)
Inscribed circle dia Peripheral cutting edge
サライ刃(ワイパー) P(Meriapihne crault tciuntgti negd gedeg)e
サFlラat イdra刃g((wワipeイr) パー) チャンファー (Main cutting edge)
サFlaラt dイra刃g((wiワpeイr) パー) チCャhaンmfフerァー
Flat drag(wiper) チChャaンmfフerァー
Chamfer
サライ刃の役割 Role of flat drag
サライ刃は仕上専用刃です。The flat drag is a dedicated finishing cutter.
コーナ R のインサートでは、送りマークがノコ刃状に付きますが、
rε w ワイパー付きインサートでは平らな面が生成できます。
rε w
W If cut with a corner R insert, cut surface is marked in wave form. But with a
R insert with a wiper, finish surface is flat.
サライ刃の幅(w)はカッタ 1 回転当たりの送り量以上の幅にします。
例えば、
刃数6枚、一刃当たりの送りをfzとすると
w≧ fz× 6 となります。
これはインサートやカッタの精度によりセットされたインサートに
多少高さのバラツキが生じても最も突き出たインサートのサライ刃
のみで、回転当たりの平面を出せるようにするためです。
通常サライ刃の幅は 1.2 〜 2.0 ㎜にします。
Set the width of flat drag (w) to the same or more size of feeding amount per
rotation of the cutter.
f e.g.
z fz fz fz fz fz
f If a feed per cutter of 6 flutes is fz, the proper width can be calculated as :
z fz fz fz fz fz
fz fz fz fz fz fz w ≧ fz × 6
w Even if the height of several inserts, each of which was reset according to the
w insert or cutter accuracy, differ from each other, a flat drag of the highest
W insert can produce a flat finish surface.
Generally set the width of a flat drag to 1.2 to 2.0 mm.
チャンファーの役割 Role of chamfer
チャンファーは、インサートの欠け防止と仕上げ面向上の効果があります。
Chamfering is made to protect the surface from chipping and also to finish the surface well.
外周切れ刃とサライ刃の中間にチャンファ
ーと呼ばれる副切れ刃を付けます。
ストレートタイプで幅0.5〜1.0㎜付けます。
技
術 R タイプは R0.8 〜 R1.2 にします。
資 Set an auxiliary cutting edge called chamfer
料 between peripheral cutting edge and flat drag.
Set 0.5 to 1.0mm width for straight type.
Set R 0.8 to R 1.2 for R type.
刃 チャンファー無し
先 (ピンカド) ストレートチャンファー Rチャンファー
交 Without chamfer Straight chamfer R Chamfer
換 (Pin corner)
式
工 弱 刃先強度 強
具 Low Nose strength High
悪 仕上げ面 良
NG Finish surface OK
I12
Page14
ホーニングの役割 Role of honing
ホーニングは刃先の強度をアップさせます。
By honing , strenght of cutting edge is increased.
刃先ホーニングにはチャンファーホーニングと丸ホーニングがあり
ますが、フライス用インサートではチャンファーホーニングが主流
ホーニング幅 ホーニング幅 です。
Honing width Honing width ホーニング角は15〜25°、ホーニング幅は1刃送りの約半分で0.1㎜
〜0.2㎜ですが、仕上刃となるサライ刃は0.03〜0.01㎜にします。
ホーニング幅 ホーニング幅
HHoonniningg w wididthth HHoonn
な
iningg
お
w w
、
ididthth
アルミニウムや鋳鉄等溶着しやすい被削材向けには通常ホー
ニングは付けません。
Nose honing can be divided into chamfer honing and round honing.
For milling insert, chamfer honing is mainly used.
ホーニング角 rε A proper honing angle is 15 to 25° honing width is 0.1 to 0.2mm that is almost
Honing angle one half of feed per 1 cutting. In case of flat drag, which is for finish cutting, set
its honing angle to 0.03 to 0.1mm.
No honing angle is required for cutter that is used for cutting any material that is
チャンファーホーニングホーニン丸グ角ホーニング rrε easily welding, like aluminium or cast iron.
Chamfer honing HHoonniningg a annggleleRound honing
コーナ高さと仕上げ面 The corner height
内接円よりコーナ高さ(B)はインサートをカッタボディにセットした時の刃先高さとなります。
(B) from the inscribed circle is the height of nose when 3the insert is5 set to the cutter body.
1 2 4
インサートをカッタボディにセットし
た時の刃先高さの高低差(正面のフレ)
は通常0.02㎜〜0.03㎜となります。
1 2 3 4 5 The difference of nose height (front run-
out) likely to occur when setting the
insert to the cut ter body is 0.02 to
0.03mm.
◎ 被削材仕上面に接してい
るインサートが、傾いている
と仕上面は悪くなります。
インサートセット時、エアー
等でごみ等入らないようにセ
インサートセット不備の場合 ットする必要があります。
正常な場合のサライ刃の摩耗 のサライ刃異常摩耗 If the insert contacting the finish
surface of a work is inclined, the
Abrasion in flat drag in normal cutting. Abnormal abrasion in flat drag
when insert setting is not proper. finishing is not done well.
Carefully set the insert allowing no
dust to enter by the air blow or
other.
I13
B ±00. 13
B ±00. 13B ±00. 13
00. 2
~00. 3
000.0.22
~~000.0.33
Technical Data Indexable Tools
Page15
How to select cutting conditions for milling
フライス加工切削条件の選び方
●切削速度(vc)Cutting Speed
vc =—π×DC×n vc :切削速度 m/min Cutting speed
1000 (m/min) DC:外径 ㎜ Cutter diameter
n :回転数 min-1 Revolution
回転数(n)Revolution π:円周率 3.14 Circle ratio
n = —1000× vc
π×DC (min-1)
●送り速度(v f)Feed rate
v f = fz × z × n(㎜ /min) vf:送り速度 ㎜ /min Feed rate
z :刃数 Number of flutes
1 刃当りの送り(fz)Feed rate per tooth n:回転数 min-1 Revolution
fz:1 刃当りの送り ㎜ /t Feed per tooth
fz =—v f
z × n (㎜ /t)
●加工時間(Tc) Tc:加工時間 min Cutting time
L v f :1 分間当りのテーブル送り速度 ㎜ /min
Tc =—v f (min) Feed rate per minute of table
L :テーブル総送り長さ(被削材長さ+フライス直径)㎜
Overall table feed length (workpiece length + grinder dia.)
●切りくず排出量(Q) Q :切りくず排出量 cm3/min ap:切込み深さ ㎜
Q =—a
Chip removal volume Cutting depth
p×ae×v f
1000 (cm3/min) ae:切削幅 ㎜ v f:1 分間当りのテーブル送り速度 ㎜ /min
Cutting width Feed rate per minute of table
●切削動力(Pc)Cutting power Pc:切削動力 kW ap:切込み深さ ㎜
Cutting power (horsepower) Cutting depth
Pc =—ap×ae×vf×kc ae :切削幅 ㎜
60× 106×η(kW) vf :送り速度 ㎜ /min
Cutting width Feed rate
η :機械効率( 0.6 〜 0.8) kc:比切削抵抗 N/㎜2
Mechanical efficiency Relative cutting resistance(下の表参照 )
Refer to the table below
kc(比切削抵抗) Specific cutting resistance
kc: Specific cutting resistance (N/mm2)
被削材材質 引張り強さ(N/㎜2)および硬さ 1刃当たりの送りに対する比切削抵抗(N/㎜2)kc for feed per tooth
Work Materials Tensile strength (N/m2) or hardness 0.1㎜/t 0.2㎜/t 0.3㎜/t 0.4㎜/t 0.6㎜/t
軟鋼
Mild Steels 520 2200 1950 1820 1700 1580
中鋼
Medium Steels 620 1980 1800 1730 1600 1570
硬鋼
Hard Steels 720 2520 2200 2040 1850 1740
670 1980 1800 1730 1700 1600
工具鋼
Tool Steels
770 2030 1800 1750 1700 1580
770 2300 2000 1880 1750 1660
クロムマンガン鋼
Chrome manganese Steels
630 2750 2300 2060 1800 1780
730 2540 2250 2140 2000 1800
クロムモリブデン鋼
Chrome molybdenum Steels
600 2180 2000 1860 1800 1670
技
術 940 2000 1800 1680 1600 1500
資 ニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼
Nickel chrome molybdenum Steels
料 352HB 2100 1900 1760 1700 1530
鋳鋼
Cast Steels 520 2800 2500 2320 2200 2040
刃 硬質鋳鉄
Hard Cast Steels 46HRC 3000 2700 2500 2400 2200
先
交 ミーハナイト鋳鉄
Meehanite Cast Steels 360 2180 2000 1750 1600 1470
換
式 ネズミ鋳鉄
Gray Cast Steels 200HB 1750 1400 1240 1050 970
工
具 黄銅
Brass 500 1150 950 800 700 630
軽合金(Al-Mg)
Light Alloy (Al-Mg) 160 580 480 400 350 320
軽合金(Al-Si)
Light Alloy (Al-Si) 200 700 600 490 450 390
I14
Page16
Cutting condition formula (milling) and trouble shooting
フライス加工におけるトラブルと原因対策
〈対 策〉 インサート材種 工 具 形 状 切 削 条 件
Insert Grade Tool Shape Cutting Condition
〈Countermeasure〉
:効果大 靱 耐 サ コ ホ す 逃 イ コ イ 刃 サ 切 送 切 切 エ
Very Effective 性 摩 ー ー ー く げ ン ー ン 数 ラ 削 り 込 削 ン
:効果あり の 耗 メ テ ニ い 角 サ ナ サ を イ 速 量 み 油 ゲ
高 性 ッ ィ ン 角 を ー 角 ー 変 刃 度 を 量 を ー
Effective い の ト ン グ を 変 ト を ト え を を 変 を か ジ
:逆効果 材 高 に グ 量 変 え を 大 を る 付 変 え 変 け 角
Not Effective 種 い す に を え る 厚 き 精 け え る え る を
:増やす、大きくする に 材 る す 変 る く く 密 る る る 小
Increase, Make it Large す 種 る え す す 級 さ
:減らす、小さくする る に る る る に く
Reduce, Make it Small す す す
る る る
トラブル項目
Troubles
逃げ面摩耗
(フランク)
Abraded Relief
Surface
(Flank)
すくい面摩耗
(クレータ)
Abraded Rake
Surface
(Crater)
衝 撃 性
チッピング
Shock Chipping
溶 着 性
チッピング
Welding Chipping
熱 亀 裂
Thermal Crack
仕 上 面
Finish Surface
び び り
Chattering
Vibration
コバ欠け・バリ
Edge Chipping,
Burr
I15
Use Tough Grade
Use Abrasion Resistant Grade
Use Cermet Material
Use coated Grode
Change The Honing Amount
Change Rake
Change Relief Angle
Make Insert Thicker
Increase Corner R
Use Precision Class Inserts
Use Inserts of Different Flute Number
Attach Flat Drag
Change Cutting Speed
Change The Feed Rate
Change Cut-In Amount
Splash Cutting Fluid
Reduce The Engage Angle
Technical Data Indexable Tools
Page17
Comparison of inserts for milling SD,SE,TE type
フライス用SD,SE,TE形標準インサートの各社形番対照表
当社標準在庫形番変更にともない各社相当形番の対照を示します。
The table indicates various model numbers of other comparison to the model numbers of standard stock items.
当社形番 精度 用途 各 社 相 当 形 番
(商品コード) Tolerance
class Application 三菱マテリアル タンガロイ 住友電工ハードメタル 京 セ ラ セコツール
Item code Mitsubishi Material Tungaloy Sumitomo Electric Hard metal Kyocera Seco Tool
SDE42TN-C9 SDEN1203AEN SDEN42ZTN
SDE42TN-C9A6 SDEN42ZTN20 SDEX42MT
E
SDE42TN-G9Y
SDE42TN-G9C3 鋼用 (
Steel SDEN42ZTNCR)
SDK42TN-C9 SDKN1203AEN SDKN42ZTN SDKN42MT SDKN1203AUTN
SDK42TN-C9A2
K
SDK42TN-B9
SDK42FN-C9 鋳鉄
Cast iron SDKN42ZFN SDKN42M SDKN1203AUFN
SDC53TN-C9
C
SDC53TN-B9
SDE53TN-C9 E 鋼用
Steel SDEN53ZTN SDEX53MT
SDK53TN-C9 SDKN1504AEN SDKN53ZTN SDKN53MT SDKN1504AUTN
SDK53TN-B9 K
SDK53FN-C9 鋳鉄
Cast iron SDKN53ZFN SDKN53M
SEE42TN-C9 SEEN42AFTN1
SEE42TN-C9Y
SEE42TN-G9 鋼用
SEE42TN-G9Y E Steel
SEE42TN-G9A2 (SEEN42AFTN24)
SEE42TN-G9C3
SEE42FN-C9 鋳鉄
Cast iron SEE42AFEN1
SEK42TN-C9 鋼用
K Steel SEKN42FTN1 SEKN42FTN SEKN42MT SEKN1203AFTN SEKN1203AFTN
SEK42FN-C9 鋳鉄
Cast iron SEKN42AFEN1 SEKN42AFFN SEKN42M SEKN1203AFFN SEKN1203AFN
SEE53TN-C9 SEEN53AFTN1
SEE53TN-C9Y 鋼用
E Steel
SEE53TN-G9Y
SEE53FN-C9 鋳鉄
Cast iron SEEN53AFEN1
SEK53TN-C9 鋼用
K Steel SEKN53AFTN1 SEKN53MT SEKN1504AFTN
SEK53FN-C9 鋳鉄
Cast iron SEKN53AFEN1 SEKN53M SEKN1504AFN
SEE42TR-G3 鋼用
E Steel SEEN42EFTR1 SEEN42EFTRCR
SEE42FR-G3 鋳鉄
Cast iron SEEN42EFER1
SEK42TR-G3 K 鋼用
Steel SEKN42EFTR1 (SEKN42EFTR) (SEK42EF3R)
TEE32TR-G0 E 鋼用
Steel TEEN32PETR1 TEEN32ZTR
TEK32TR-G0 鋼用
技
術 K Steel TEK32PT3R
TEK32FR-G0 鋳鉄 (TEK32PT3R)
資 Cast iron
料 TEE43TR-G0E 鋼用 TEEN43PETR1 TEEN43ZTR TEEN43TR TEE43PT4R
TEE43TR-G0EY E Steel
刃 TEE43FR-G0E 鋳鉄
Cast iron TEEN43PEER1 (TEEN43ZFR) (TEEN43R)
先
交 TEK43TR-G0E 鋼用
K Steel TEKN43PETR1 TEKN43TR TEK43PT4R
換 TEK43FR-G0E 鋳鉄
Cast iron TEKN43PEER1 (TEKN43R) (TEK43PT4R)
式
工 ・上表中、( )で示した形番は同一品ではありませんが、類似形状品のため参考としました。
具 ・本表は、各社の承認を得たものではありません。
・The numbers in bracket ( ) are not exactly the same model, but similar to the respective model and shown as reference.
・This table is not an official comparison table approved by each maker.
I16
Page18
Table of corresponding materials from various companies for milling
フライス加工の各社材種対応表
フライス コーティング材種 Coated materials for milling
用途 使用分類 グレード 三菱 工
当 社 マテリアル タンガロイ 住友電
ハードメタル サンドビック 京セラ ダイジェット ケナメタル セコツール
Application Use
classification Grade Mitsubishi Materials Tungaloy Sumitomo Electric Hard metal Sandvik Kyocera Dijet Kennametal Seco Tools
ATH80D
ATH08M
P01 TH308 MP8010 AH710 ACP100 GC1010 PR1525 JC8003 KC715M MP1500
PN208 MP6120 AH725 ACP200 GC1130 PR1225 JC730U KC725M MP2500
JP4105 VP15TF AH730 ACP300 GC1030 PR1230 JC8015 KC792M MP3000
PCA12M MP6130 AH3035 GC2030 PR830 JC5015 KC994M T250M
P10 PN15M
PN215 UP20M AH3135 GC2040 JC5118 T15M
JP4115 VP20RT AH110 GC3040 JC6235 T20M
CY150 VP30RT AH120 GC4220 JC5040 T25M
P P20 CY9020 F7010 AH130 GC4230 JC8050 F20M
JP4120 FH7020 AH140 GC4240 F25M
HC844 F7030 AH9030 F40M
CY25
P30 CY250 GH130
CY250V AH330
JS4045 GH330
PTH30E T3130
P40 PTH40H T313W
JS4060
GX2140
M01 PN08M
PN208 VP15TF AH120 ACM100 GC1130 PR1525 JC730U KC730M MP2500
MP9130 AH130 ACM200 GC1030 PR1535 JC835S KC725M T250M
M10 PN15M
PN215 MP9030 AH140 ACM300 GC2030 PR1225 JC8015 KC994M T20M
UP20M AH725 T250A GC2040 PR830 JC5015 T25M
M20 JP4120 VP20RT AH730 T4500A GC1040 CA6535 JC5118 F30M
HC844 MP7140 GH110 A30N GC4230 JC8050 F40M
フ M
M30 CY250 VP30RT GH130 GC4240
JS4045 F7010 AH330
ラ PTH30E F7030 GH330
PTH40H GH340
JM4160
イ M40 AH3135
GX2160
AX2040 T3130
ス ATH80D
K01 ATH08M
TH308 MP8010 GH110 ACK200 GC1010 PR1510 JC8003 KC915M MK1500
VP15TF AH110 ACK300 GC1020 PR1210 JC605W KC920M MK2000
ATH10E VP20RT AH725 GC3330 CA420M JC600 KC925M MK3000
K10 TH315
CY100H MC5020 AH120 GC3040 JC608X KC992M T150M
GH130 GC3220 JC6610 KC930M T250M
K CY9020 AH330 GC4220 JC8015 F15M
CY150
K20 PTH13S T1115 GC4230 JC5015 MP1500
JP4120 GC4240 JC6235
GX2120 K15W JC5080
CY250 K20D
K30 JS4045 K20W
GX2040
N01 PN08M
PN208
LC15TF DS1100 DL1000 GC1130 PDL025 JDA30
CY100H
DS1200 DA1000 GC1030 KPD001 JDA735
N10 PTH13S
N SD5010 CD10 KPD010 JDA10
HD7010 KPD230 JDA715
N20 KPD250
N30
S01 PN08M
PN208 MP9120 ACM100 GC1130 PR1535 JC8003
VP15TF ACM200 GC1030 PR1210 JC8015
S10 JP4120
S JS1025 MP9130 ACM300 GC2030 CA6535 JC5015
MP9030 GC2040 KPD001 JC5118
S20 PTH30H KPD010 JC835S
S30 JM4160 JC8050
H01
ATH80D MP8010 GC1010 DH102
ATH08M VP15TF GC1130 DH103
PTH08M
H10 TH308 GC1030 JC6102
H JP4105 GC3040 JC8003
BH200
BH250 GC4220 JC8008
H20 TH315 JC8015
JP4115 JC5118
H30 JP4120
注)本表は、各社の承認を得たものではありません。 Note: This table has not been approved by the individual companies.
I17
Milling
Technical Data Indexable Tools
Page19
Table of corresponding materials from various companies for milling
フライス加工の各社材種対応表
超硬合金材種 Carbide alloy materials
使用分類 グレード 三菱
当 社 タンガロイ 住友電工 サンドビック 京セラ ダイジェット ケナメタル セコツール
マテリアル ハードメタル
Application Grade Mitsubishi Materials Tungaloy Sumitomo Electric Hard metal Sandvik Kyocera Dijet Kennameral Seco Tools
WS10 STi10T TX10S ST10P S1P SR10 K5H S10M
P10 SRT K45
EX35 STi10 TX20 ST20E SMA SRT K29 S25M
P20 TX25 SR20 K45
UX25 DX30 K2885
P EX35 TX30 A30 SM30 PW30 SR30 K420 S25M
P30 UX30 A30N DX30 KM
DX25 K21
EX35 TX40 ST40E S6 SR30 K420 S60M
P40 DX35 KM
GX
WA10B TU10 U10E H10A UMN S10M
M10 UM10
EX35 UTi20T TU20 U2 H13A UM20 K313 HX
M M20 DX25 K40
DTU PVA
EX35
M30 UTi20T UX30 A30 H10F PW30 DTU K2885 HX
A30N UMS K2S
WH01 HTi05T TH03 H2 H1P KG03
K01 WH05 H1
WH10 HTi10 TH10 EH10 H10 KW10 KG10 K6 HX
EH510 HM KT9 K313
K K10 CR1 K68
KM1
WH20 HTi20T G2 G10E H13A KG20 K1 883
K20 KS20 EH20 KT9 K8735
EH520 CR1
NM08 F F0 FB10
Z01 AF0
F1
NM15 MF10 M A1 FB10
超微粒 Z10 EM10 AF1 FB15
超硬合金
Ultra-molecular
carbide alloy EF20N TF15 EM20 FB15
Z20 UF20 UM FB20
UF30 UM FB20
Z30
サーメット材種 Cermet materials
使用分類 グレード 三菱 住友電工
当 社 タンガロイ サンドビック 京セラ ダイジェット ケナメタル セコツール
マテリアル ハードメタル
Application Grade Mitsubishi Material Tungaloy Sumitomo Electric Hard Metal Sandvik Kyocera Dijet Kennameral Seco Tools
CH350 AP25N NS520 T110A TN30 LN10 KT125
NX2525 AT520 T2000Z PV30 CX50 HTX
P10 AT530 T1200A NIT
CX75
旋削用 CH550 AP25N NS530 T2000Z CT515 TN60 CX50 KT315 CM
技 for Turning NX2525 AT530 T1200A CT520 TN6020 NAT KT175
術 P20
UP35N GT530 T130A CT5015 PV60 CX75 HT2
資
料 NX335 T3000Z CT525 PV7020
CH570
P30 VP45N NS530 T3000Z GC1525 PV90 CX90 CR
NS540 CT525 CX99
刃 CH550 NX2525 NS530 T12A TN60 NIT KT530M CM15
先 P10 MZ1000 CX75 KT195M
交 CH7030 NX2525 NS530 T250A CT520 TN60 NAT KT530 CM15
換
式 フライス用 TN100M CX75 HT7
P20
工 for Milling CX90 KT605
具 SUZ
NX4545 NS540 T250A CT530 CX90 CM15
P30 CH7035 CX99
注)本表は、各社の承認を得たものではありません。 Note: This table has not been approved by the individual companies.
I18
Page20
Nomenclature of turning tools parts and role of nose angle
旋削工具各部の名称と刃先角度の役割
各部の名称 Name of parts of Turning Tools
横すくい角
Orthogonal rake angle 全 長
Overall Length
前切れ刃角 End cutting edge angle
横逃げ角 シャンク幅
Orthogonal clearance angle Shank width
ノーズ半径
Nose radius 横切れ刃角
Side cutting edge angle
前すくい角
切れ刃高さ (切れ刃傾き角)
Nose height Cutting edge Inelintion
シャンク高さ
Shank height
前逃げ角 Normal clearance angle
バイトホルダ横切れ刃角の影響 Effect of side Edge cutting Angle
横切れ刃角:0゜ Side cutting edge angle : 0 ゜ 横切れ刃角:30゜ Side cutting edge angle : 30 ゚
(f ㎜/rev) (f ㎜/rev)
P P y
P Px
h h
30°
0°
被削材と接触長さが短くなるため厚くて幅の狭い切りくずが出 被削材との接触長さが長くなるため薄くて幅の広い切り
ます。 くずが出て、被削材を押す分力Pyが発生します。
Thick and narrow chips are produced,because the contact length of an Insert and Thin and wide chips are produced, because the contact length of an Insert
work material is short. and work material, Force Py,which pushes work piece, are produced.
● 切削性能に及ぼす影響 Effect on cutting performance
項目 小 Small 横切れ刃角 Side cutting edge angle 大 Large
Elements
刃先の摩耗率 大 小
Wear Large Small
被削材 削りやすい材料 削りにくい材料
Work material Large
Easy-to -machine materials Difficult-to-machine materials
切削動力 小 大
Cutting force Small Large
びびり 出にくい 出やすい
Vibration Not likely Likely
Difficult to be produced Easy to be produced
切削方法 仕上 荒
Application Finishing Roughing
被削材剛性 細くて長い物 太い物
Rigidity of work piece Small/Long Big
機械剛性 剛性低い場合 剛性高い場合
Mechanical rigidity Low rigidity High rigidity
切りくず処理性 良い 悪い
Chips rejectability Good Bad
I19
Technical Data Turning Tools